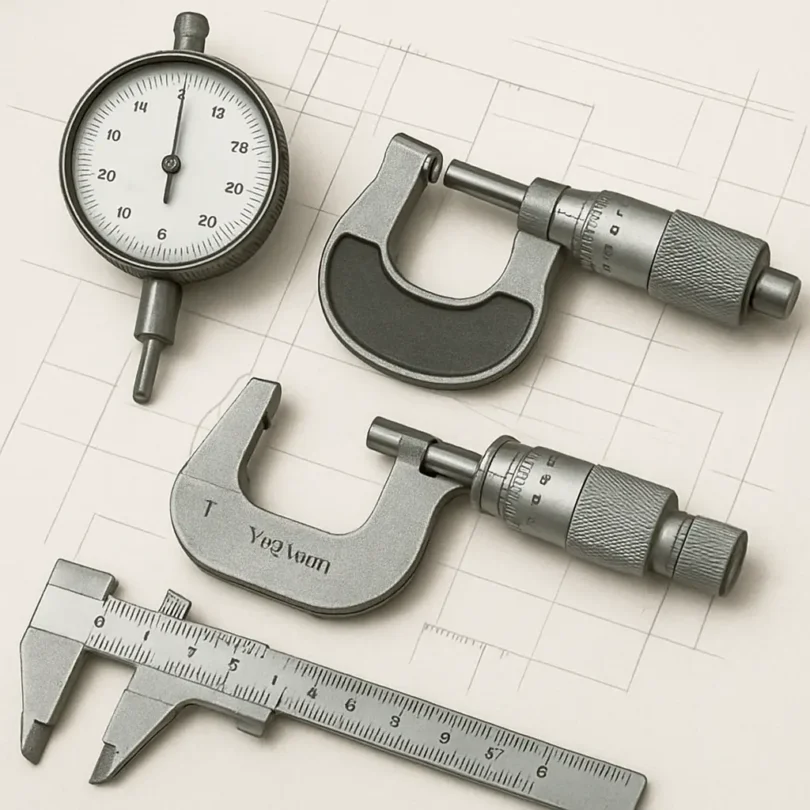
In a world increasingly driven by precision and accuracy, the process of “kalibraatio” or calibration becomes more vital than ever. The demand for exactness in measurements transcends various domains, from scientific research to industrial manufacturing, underscoring the critical role calibration plays in our lives. Whether in science or industry, understanding the importance of calibration and how it impacts our daily lives can help us appreciate its role in maintaining quality and reliability. As technology progresses and industries evolve, the need for precise calibration continues to grow, ensuring that innovations are both safe and effective.
Kalibraatio ensures that instruments deliver accurate readings and supports process integrity across various sectors. By implementing strict kalibraatio practices, industries maintain consistency in their products and services, fostering trust and reliability. This essential process drives the operational excellence that modern industries demand—and its relevance continues to grow.
What is Calibration?
Calibration, or “kalibraatio,” involves comparing an instrument’s measurements to a known standard to confirm accuracy and consistency. Professionals across fields like medicine, manufacturing, and environmental science rely on calibration to ensure safety, quality, and compliance. In essence, calibration acts as a quality assurance tool that validates the precision of measurement instruments and protects the integrity of data and results.
Calibration isn’t confined to technical fields—it plays a role in everyday life. Whether you’re checking your home thermostat or confirming that your car’s speedometer shows the right speed, calibration helps ensure accuracy. By following regular calibration routines, both individuals and organizations can catch errors early, cut down on waste, and boost performance leading to a more efficient and reliable environment.
The calibration process generally involves several key steps to ensure accuracy and reliability. Each step is critical to achieving a precise and dependable outcome.
Preparation
Before beginning calibration, gather all necessary tools, documentation, and equipment. Ensure that the instrument to be calibrated is in good working condition. This stage involves verifying that all calibration tools are themselves calibrated and certified to provide accurate standards. It is essential to create a controlled environment to minimize external factors that could influence the calibration process.
Measurement
Compare the instrument’s readings to a known standard or reference. This step often involves using a calibration device that provides a precise measurement for comparison. It is crucial to conduct multiple measurements under varying conditions to ensure the instrument’s reliability across different scenarios. This thorough approach helps in identifying any inconsistencies that may not be evident in a single test.
Adjustment
If discrepancies are found, adjust the instrument to align with the standard. This may involve mechanical adjustments or software updates. The adjustment process should be meticulously documented to track changes and ensure that future calibrations can be carried out efficiently. It is important to follow manufacturer guidelines and industry standards to avoid compromising the instrument’s integrity.
Documentation
Record the calibration process, including any adjustments made. This documentation is essentialfor maintaining a calibration history and for future reference. Keeping detailed records supports traceability and accountability, enabling organizations to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards. Proper documentation also facilitates easier troubleshooting and maintenance in the future.
Verification
After adjustments, recheck the instrument to ensure it meets the required standards and specifications. This final step confirms that the calibration process has been successful and that the instrument is ready for use. Verification provides an additional layer of assurance, reinforcing the reliability of the instrument’s measurements and fostering confidence in its performance.

Importance of Calibration in Science and Industry
Calibration plays a pivotal role in both science and industry. Here are some key reasons why it is essential:
Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability
In fields like healthcare and pharmaceuticals, where precision is critical, professionals rely on Kalibraatio to ensure instrument accuracy. This accuracy is essential for diagnostics, treatment, and research. A faulty medical reading can lead to misdiagnosis or incorrect treatment—highlighting the life-saving value of proper kalibraatio. In research, precise data supports scientific breakthroughs and fuels technological innovation.
Calibration also boosts reliability by helping instruments maintain consistent performance over time. This consistency is crucial for longitudinal studies and ongoing industrial processes, where even small deviations can lead to serious consequences. By preserving both accuracy and reliability, calibration builds trust in the results—an essential factor for driving scientific progress and achieving industrial success.
Compliance with Standards
Industries follow international and national standards to ensure product quality and safety. Kalibraatio helps businesses meet these benchmarks, avoid costly fines, and safeguard their reputation. Beyond legal compliance, effective kalibraatio gives companies a competitive edge by demonstrating their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
Regular calibration keeps products and services aligned with industry benchmarks, boosting market confidence and strengthening customer loyalty. When companies follow these standards, they reduce the risk of recalls, avoid legal issues, and protect their brand reputation—ultimately securing their position in a competitive market.
Enhancing Product Quality
In manufacturing, teams rely on kalibraatio to ensure equipment produces products within precise tolerances. This consistency leads to high-quality results and reduces the risk of defects. By delivering reliable products, manufacturers meet customer expectations while cutting waste and lowering costs tied to rework and scrap.
Calibration also plays a role in innovation, as it supports the development of new products by ensuring that prototypes and production models meet design specifications. By fostering a culture of quality through calibration, manufacturers can drive innovation while maintaining the highest standards of excellence.
Safety Assurance
In sectors like aviation and automotive, safety takes top priority. Teams rely on kalibraatio to ensure instruments deliver accurate, reliable data—minimizing risks and enhancing safety. These instruments track critical factors like engine performance and environmental conditions, both of which directly impact operational safety.
When industries regularly calibrate their instruments, they reduce the risk of accidents and prevent failures that could lead to catastrophic consequences. Calibration also helps companies stay compliant with regulations—an essential step for maintaining licenses and certifications—reinforcing its critical role in protecting public safety.
Techniques in Calibration
The methods used in calibration can vary depending on the instrument and industry. Here are some common techniques:
Mechanical Calibration
Kalibraatio in mechanical systems involves adjusting an instrument’s physical components. Technicians may align parts or fine-tune tension and pressure settings. This form of calibration is essential for instruments that measure physical movement or force—such as scales, torque wrenches, and pressure gauges.
Regular mechanical calibration is necessary to account for wear and tear, which can affect the accuracy of measurements over time. By ensuring that mechanical components are properly calibrated, industries can maintain the precision and reliability of their instruments, leading to improved performance and longevity.
Electrical Calibration
This method checks and adjusts the electrical output of devices, especially those that measure voltage, current, or resistance. Technicians use electrical calibration to ensure electronic devices operate within defined parameters—crucial for maintaining both performance and safety.
In industries like telecommunications and electronics manufacturing, accurate electrical calibration plays a key role in preserving signal integrity and ensuring device functionality. When companies regularly calibrate their electrical instruments, they minimize the risk of malfunctions and improve the overall quality of their electronic products.
Thermal Calibration
In industries where temperature plays a critical role, thermal calibration keeps temperature measurements accurate. Technicians compare instrument readings with a known temperature standard to verify precision. This accuracy is vital for processes that depend on strict temperature control, such as food processing and chemical manufacturing.
When industries calibrate temperature-sensitive instruments, they maintain product quality and safety, prevent spoilage, and improve energy efficiency. Thermal calibration also helps companies comply with environmental regulations—an increasingly important priority in today’s sustainability-driven world.
Chemical Calibration
In laboratories, chemical calibration enables analytical instruments to deliver accurate readings. Technicians use standard solutions to verify each instrument’s performance. This essential process validates experimental results and preserves the integrity of laboratory work.
Accurate chemical calibration fuels research and development by providing reliable data to test hypotheses and develop new compounds. When laboratories regularly calibrate their analytical instruments, they directly advance scientific innovation while upholding strict standards for safety and accuracy.

The Future of Calibration Technology
As technology advances, so does the field of calibration. Here are some trends and innovations shaping the future of calibration:
Automation and AI
Automation and artificial intelligence streamline the calibration process. Automated systems handle calibrations faster and with fewer human errors. AI predicts when instruments need recalibration, while machine learning algorithms enhance precision by analyzing large data sets and detecting patterns that people might overlook.
These advancements make calibration processes more efficient and cost-effective, cutting downtime and boosting productivity. When industries adopt automation and AI, they strengthen their calibration practices and stay at the forefront of technological innovation.
Digital Calibration
Digital calibration uses software and digital tools to perform and record calibrations. This method enhances accuracy and provides a more efficient way to manage calibration data. Digital tools can store calibration records in the cloud, enabling easy access and retrieval of data for audits and compliance checks.
The digitalization of calibration processes also facilitates real-time monitoring and analysis, allowing for immediate adjustments and improvements. By embracing digital calibration, companies can improve their operational efficiency and ensure that their calibration practices meet the demands of a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Remote Calibration
With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), remote calibration has become more feasible. Devices can be calibrated from afar, saving time and resources, especially in large-scale operations. Remote calibration enables companies to manage their calibration activities across multiple locations without the need for physical intervention, reducing travel costs and minimizing disruptions.
This approach is particularly beneficial for industries with geographically dispersed operations, such as oil and gas or telecommunications. By leveraging remote calibration, companies can enhance their flexibility and responsiveness, ensuring that their calibration practices keep pace with the demands of a connected world.
Sustainable Practices
As industries become more environmentally conscious, sustainable calibration practices are emerging. These include using eco-friendly materials and reducing waste in the calibration process. Sustainable calibration practices also involve optimizing energy use and minimizing the environmental impact of calibration activities.
By adopting sustainable practices, companies can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change. Embracing sustainability in calibration not only supports environmental goals but also enhances brand reputation and meets the expectations of increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
Conclusion
Calibration, or “kalibraatio,” is an essential process in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of instruments across various sectors. From enhancing safety to improving product quality, the benefits of calibration are far-reaching. As technology evolves, so too will the methods and techniques used in calibration, promising even greater precision and efficiency in the future.
By understanding and implementing effective calibration strategies, industries can continue to thrive in a world where precision is key. Whether through traditional methods or embracing new technologies, the importance of calibration cannot be overstated. As we look to the future, calibration will remain a cornerstone of quality and innovation, supporting the advancement of technology and the betterment of society as a whole.